
The docker -compose CLI utility allows users to run commands on multiple containers at once, for example, building images, scaling containers, running containers that were stopped, and more. It uses YAML files to configure the application's services and performs the creation and start-up process of all the containers with a single command.
Docker network type download#
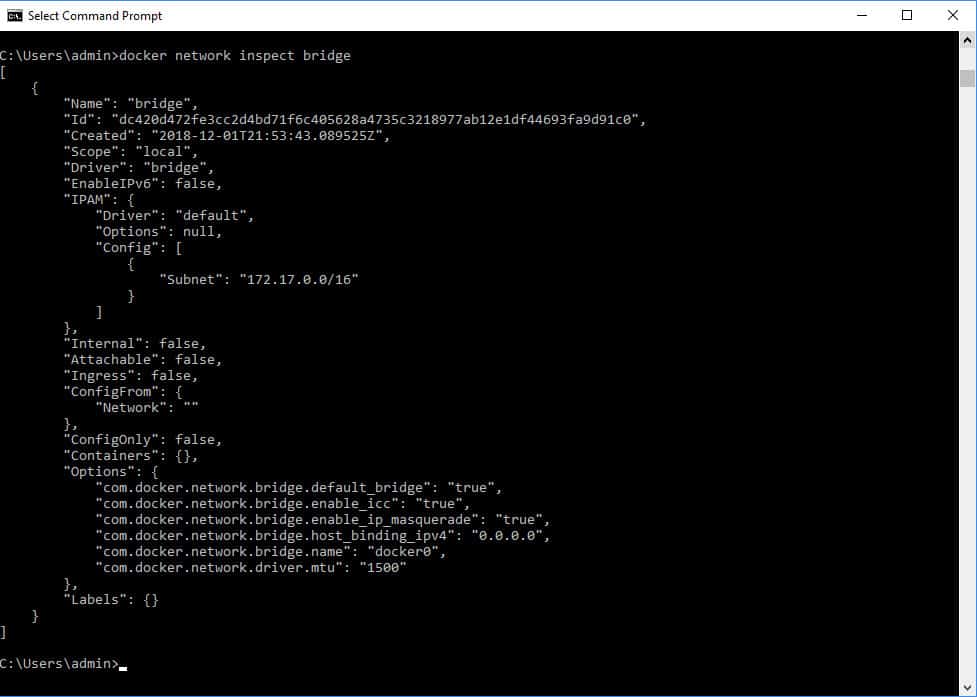
Docker clients connect to registries to download ("pull") images for use or upload ("push") images that they have built. Registries: A Docker registry is a repository for Docker images.The result is known as a swarm, a set of cooperating daemons that communicate through the Docker API. A Docker service allows containers to be scaled across multiple Docker daemons.Images are used to store and ship applications. A Docker image is a read-only template used to build containers.A container is managed using the Docker API or CLI. A Docker container is a standardized, encapsulated environment that runs applications.The main classes of Docker objects are images, containers, and services. Objects: Docker objects are various entities used to assemble an application in Docker.The Docker client program, called docker, provides a command-line interface (CLI), that allows users to interact with Docker daemons. The daemon listens for requests sent via the Docker Engine API. Software: The Docker daemon, called dockerd, is a persistent process that manages Docker containers and handles container objects.
Docker network type software#
The Docker software as a service offering consists of three components: Docker containers are standard processes, so it is possible to use kernel features to monitor their execution - including for example the use of tools like strace to observe and intercede with system calls. ĭocker implements a high-level API to provide lightweight containers that run processes in isolation. Since version 0.9, Docker includes its own component (called " libcontainer") to use virtualization facilities provided directly by the Linux kernel, in addition to using abstracted virtualization interfaces via libvirt, LXC and systemd-nspawn. The Linux kernel's support for namespaces mostly isolates an application's view of the operating environment, including process trees, network, user IDs and mounted file systems, while the kernel's cgroups provide resource limiting for memory and CPU. A 2018 analysis found that a typical Docker use case involves running eight containers per host, and that a quarter of analyzed organizations run 18 or more per host. īecause Docker containers are lightweight, a single server or virtual machine can run several containers simultaneously.

Docker on macOS uses a Linux virtual machine to run the containers.
When running on Linux, Docker uses the resource isolation features of the Linux kernel (such as cgroups and kernel namespaces) and a union-capable file system (such as OverlayFS) to allow containers to run within a single Linux instance, avoiding the overhead of starting and maintaining virtual machines. This enables the application to run in a variety of locations, such as on-premises, in public or private cloud. ĭocker can package an application and its dependencies in a virtual container that can run on any Linux, Windows, or macOS computer. Docker can use different interfaces to access virtualization features of the Linux kernel.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
